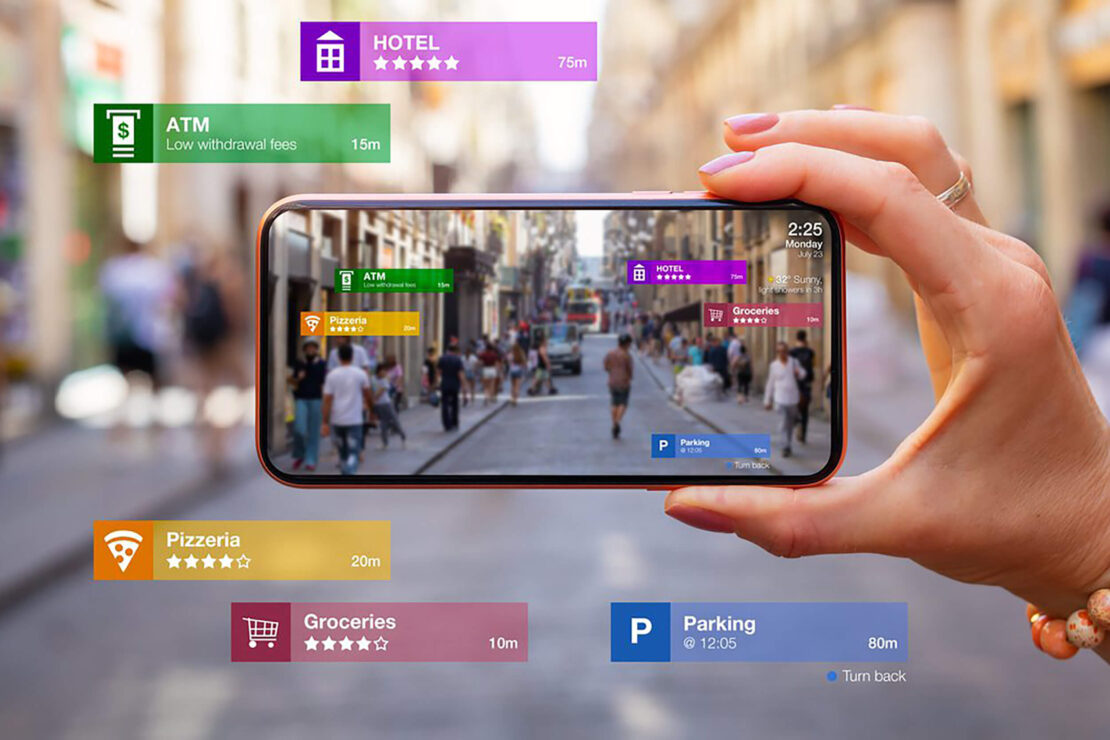
Augmented Reality (AR) is a revolutionary technology that blends digital content with the real world, providing users with an enhanced and immersive experience. Unlike Virtual Reality (VR), which creates a completely artificial environment, AR overlays digital information onto the physical environment in real-time. This article explores the various aspects of AR, including its history, applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends.
Introduction to Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality (AR) refers to the technology that superimposes digital content, such as images, videos, or 3D models, onto the user’s view of the real world. By using a smartphone, tablet, or specialized AR device, users can interact with virtual objects as if they exist in their physical surroundings. AR enhances the user’s perception of reality by adding digital elements that are seamlessly integrated into their environment.
History of Augmented Reality
The concept of Augmented Reality dates back to the 1960s, with the development of early head-mounted displays and computer-generated graphics. However, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that AR technology began to gain traction, thanks to advancements in computer vision, graphics processing, and mobile computing. Today, AR has become a mainstream technology, with applications across various industries and sectors.
Applications of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality has a wide range of applications, spanning from entertainment and gaming to education, healthcare, retail, marketing, architecture, and design. In the entertainment industry, AR has revolutionized gaming experiences with popular titles like Pokémon GO, which blend virtual creatures with real-world environments. In education and training, AR enables immersive learning experiences by overlaying educational content onto textbooks, worksheets, or physical objects. In healthcare, AR technology is used for surgical planning, medical imaging, patient education, and rehabilitation. In retail and marketing, AR enhances customer engagement and shopping experiences by allowing consumers to visualize products in their own space before making a purchase.
Types of Augmented Reality
There are several types of Augmented Reality, each with its own set of technologies and applications. Marker-based AR relies on visual markers, such as QR codes or image targets, to anchor digital content in the real world. Markerless AR, also known as location-based AR, uses GPS, compass, and accelerometer data to position virtual objects in physical space. Projection-based AR projects digital images onto real-world surfaces, creating interactive displays or installations. Superimposition-based AR overlays digital content onto the user’s view of the real world, without the need for special markers or sensors.
Benefits of Augmented Reality
Augmented Reality offers numerous benefits, both for businesses and consumers. For businesses, AR provides a unique platform for showcasing products and services, engaging customers, and driving sales. For consumers, AR enhances the shopping experience, facilitates learning and exploration, and enables new forms of entertainment and social interaction. By bridging the gap between the physical and digital worlds, AR creates immersive and interactive experiences that captivate and delight users.
Challenges and Limitations of Augmented Reality
Despite its potential, Augmented Reality faces several challenges and limitations, including technical constraints, privacy concerns, integration issues, and cost barriers. Technical limitations, such as limited field of view, latency, and accuracy, can affect the quality and performance of AR applications. Privacy and security concerns arise from the collection and storage of user data, as well as the potential for unauthorized access or misuse of personal information. Integration challenges arise from the need to seamlessly integrate AR technology with existing hardware, software, and infrastructure. Cost barriers, such as the high cost of AR devices and development tools, can limit the adoption and scalability of AR solutions.
Future Trends in Augmented Reality
Despite these challenges, Augmented Reality is poised for significant growth and innovation in the coming years. Advances in AR technology, such as improved sensors, displays, and processing power, will enable more immersive and realistic experiences. The growth of the AR market will drive investment and innovation in AR hardware, software, and content creation tools. Integration with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and 5G connectivity, will unlock new opportunities for AR applications and services. As AR becomes more ubiquitous and accessible, it will continue to reshape industries, transform user experiences, and redefine the way we interact with the world around us.
Augmented Reality vs. Virtual Reality
While Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality share some similarities, they are fundamentally different technologies with unique features and applications. Augmented Reality overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of reality. Virtual Reality, on the other hand, creates a completely artificial environment that immerses the user in a virtual world. While AR enhances the user’s existing environment, VR transports the user to a new and immersive digital environment. Both AR and VR have their own strengths and weaknesses, and they are often used in complementary ways to create immersive and engaging experiences.
Augmented Reality Devices
Augmented Reality experiences can be accessed through a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart glasses, and head-mounted displays. Smartphones and tablets are the most common AR platforms, thanks to their widespread adoption and powerful processing capabilities. Smart glasses and headsets, such as the Microsoft HoloLens, Google Glass, and Magic Leap One, offer more immersive and hands-free AR experiences. Wearable AR devices, such as AR contact lenses and smart clothing, are still in the early stages of development but hold promise for the future of AR technology.
Examples of Successful Augmented Reality Implementations
Augmented Reality has already been successfully implemented in a wide range of industries and applications. In the gaming industry, Pokémon GO became a global phenomenon by blending AR technology with the beloved Pokémon franchise. Snapchat filters use AR to overlay digital effects onto users’ faces in real-time, enabling fun and interactive communication. The IKEA Place app allows users to visualize furniture and home décor in their own space before making a purchase, enhancing the shopping experience. Microsoft HoloLens is used in architecture and design to create immersive virtual prototypes and walkthroughs of buildings and structures.
Impact of Augmented Reality on Industries
Augmented Reality has the potential to transform industries and sectors, ranging from retail and healthcare to education and entertainment. In the retail industry, AR enables virtual try-on experiences, product visualizations, and interactive shopping assistants, driving sales and customer engagement. In healthcare, AR is used for medical training, surgical planning, patient education, and remote assistance, improving patient outcomes and reducing medical errors. In education, AR enhances learning experiences by providing interactive and immersive content that engages students and facilitates comprehension. In entertainment, AR offers new forms of storytelling, gaming, and social interaction, creating memorable and engaging experiences for users.
Ethical Considerations in Augmented Reality
As Augmented Reality becomes more pervasive, it raises important ethical considerations and challenges. Privacy issues arise from the collection, storage, and use of personal data in AR applications, such as location tracking, biometric data, and user preferences. Data security is a critical concern, as AR devices and applications may be vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and cyber attacks. Content moderation is another challenge, as AR experiences may include user-generated content that is inappropriate, offensive, or harmful. Developers and policymakers must address these ethical considerations to ensure that AR technology is used responsibly and ethically.
The Future of Augmented Reality
Looking ahead, Augmented Reality holds tremendous promise for the future, with ongoing advancements in technology, adoption, and innovation. Integration with artificial intelligence will enable more intelligent and context-aware AR experiences that adapt to users’ preferences and behaviors. The evolution of AR hardware, such as lightweight and affordable smart glasses, will make AR more accessible and ubiquitous. Social and cultural implications of AR will continue to evolve, shaping how we interact with technology, society, and the world around us. As Augmented Reality becomes increasingly integrated into our daily lives, it will empower individuals and organizations to create, communicate, and collaborate in new and exciting ways.
MirrAR: Transforming the Shopping Experience
MirrAR is a pioneering platform that embodies the concept of virtual stores and takes it to the next level. By leveraging AR technology and the metaverse, MirrAR offers consumers a truly immersive shopping experience unlike any other. Here’s how MirrAR works:
AR-Powered Try-On: MirrAR allows users to try on virtual clothing and accessories using AR technology. By simply pointing their smartphone camera at themselves, users can see how different outfits look on their body, helping them make more confident purchasing decisions.
Virtual Home Decor: MirrAR enables users to visualize furniture and home decor items in their own living spaces. By placing virtual furniture models in their room using AR, users can see how different pieces would look and fit, eliminating the guesswork associated with online furniture shopping.
Metaverse Integration: MirrAR seamlessly integrates with the metaverse, allowing users to explore virtual environments and interact with brands and products in a highly immersive manner. Within the MirrAR metaverse, users can personalize their avatars, socialize with friends, and discover new products in a dynamic and interactive setting.
Conclusion
Augmented Reality is a transformative technology that enhances our perception of reality by overlaying digital content onto the physical world. With its wide range of applications, benefits, and opportunities, AR is poised to revolutionize industries, reshape user experiences, and redefine the way we interact with technology. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and responsible use, we can unlock the full potential of Augmented Reality and create a brighter future for all.
